Created Samstag 15 März 2025
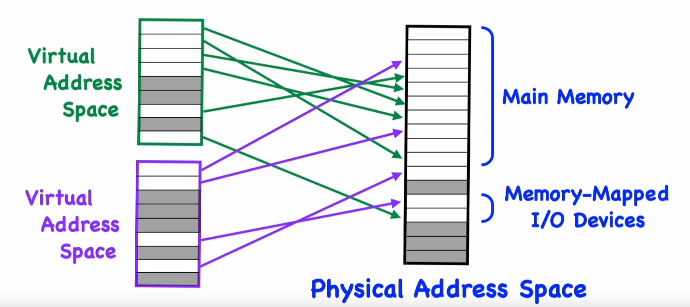
Virtual pages to Physical pages
Page table
Address mapping
This concept based on RISC-V Sv32. Besides the hw details, it should be the same with other architectures but with less legacy baggage.
E.g. RISC-V opitions
RV32 (32-bit CPUs)
- No mapping (paging turned off)
- Sv32: 32-bit virtual address -> 34-bit physical address (e.g. 16 GiB RAM) -> 2-level trees
RV64 (64-bit CPUs)
- No mapping (paging turned off)
- Sv39: 39-bit virtual address -> 56-bit physical address (e.g. 0.5 TiB RAM) -> 3-level trees
- Sv48: 48-bit virtual address -> 56-bit physical address (e.g. 256 TiB RAM) -> 4-level trees
- Sv57: 57-bit virtual address -> 56-bit physical address (e.g. 128 PiB RAM) -> 5-level trees
For each address space
Implementation: Page Table
A data sturcture im physical memory. Hardware reads this data structure on every memory access.
Optimization
Translation Lookaside Buffers (TLB): Cache of important recentl-used entries.
Protection bits
R/W/X Read/Write/Execute, Each page has priviliges which allows one of the commands LOAD, STORE or FETCH -> page faults if the wrong access is used.
V Is page valid (in use, in phys. memory)? -> page faults (invalid = unmapped pages)
U Is this a User page or a Supervisor page? -> page faults
U-mode:
access U page -> OK, access S page -> page faults
To give access (e.g. data to/from User pages by supervisor code) there is a status register sstatus. SUM bilts allow LOAD/STORE operations.
Pages
Each page is 4 KBytes (212 = 4096).
Pages are aligned on 4k boundaries (memory addresses).
Offset into page: Low-order 12 bits
Upper bits of address: Page number
Address

Page table
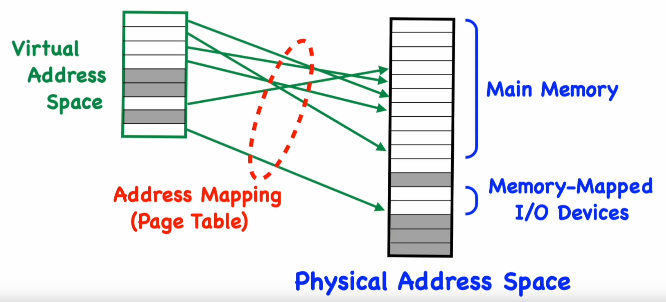
Maps virtual page number to physical page number. The offset is unchanged.
Sv32
Physical addreses
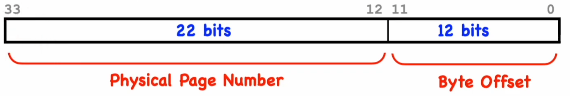
Physical memory addresses: 34 bits
Number of pages: 222 = 4M
Number of bytes per page: 4K
Max Physical addresses: 222 x 212 = 4M x 4K = 16 GiB
Mappings
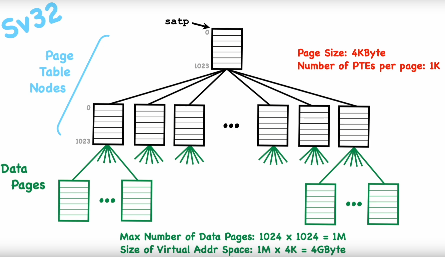
The mappings data structure will be done with keys (ordered set of integers) to values (integers) organized into a Radix Tree. Sv32 uses Two-level-tree. Each node points to 1024 (210) childern (= physical page number ) PTE: Page Table Entry, 1M x 4K = 4 GiB).
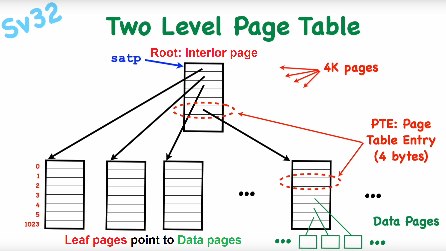
satp register Sv32
CPU register 32 bit, Supervisor Address Translation and Protection

Mode: 1bit, 0 = Enable 32bit (Sv32) page-based virtual addresssing, 1 = Enables paging -> all 32bits need to be 0 to disable paging.
ASID: 9bit, Address Space Identifier
PPN: 22bit, Physical page number (PPN, physical address devided by 4KiB) of the MMU mapping tree root node.
-> In Sv39, Sv48, and Sv57 (64bit CPUs) it is 64bit wide
Page table
Each page table entry points to an array[1024] of PTEs (4 bytes).
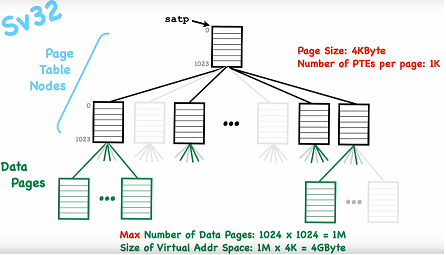
Gray pages are not used. Access them would lead to a page fault.
Page table entry (PTE)
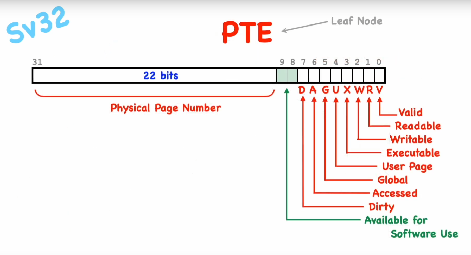
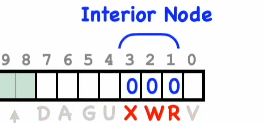
PTE entries for the interior page/node looks has the RWX bits (flags) set to 0
Virtual Addresses
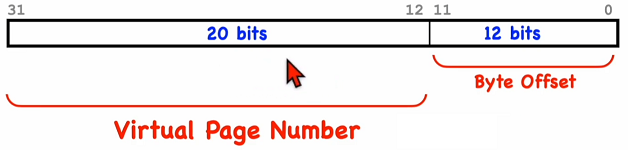
Virtual memory addresses: 32 bits
Number of pages: 220 = 1M
Number of bytes per page: 4K
Virtual space size: 220 x 212 = 1M x 4K = 4 GiB
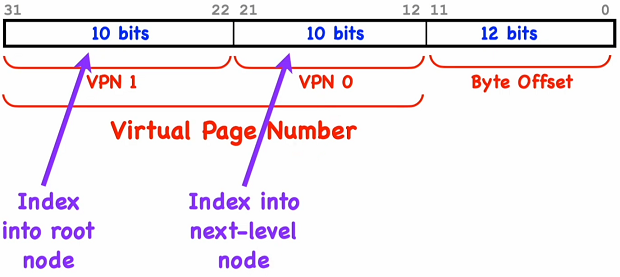
Mapping procedure
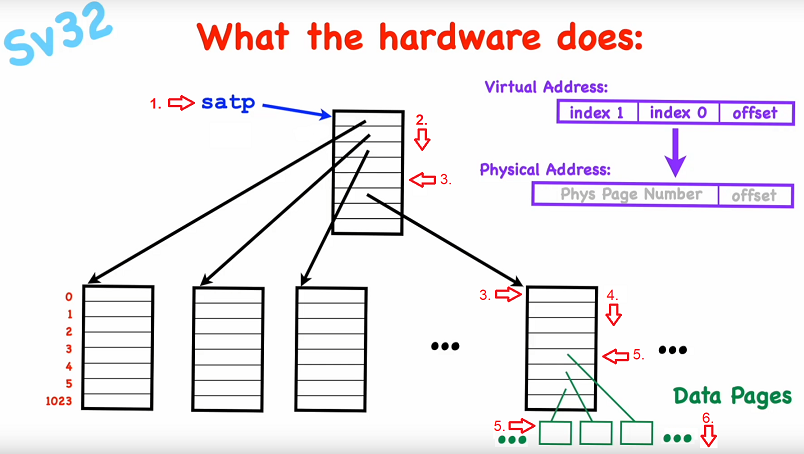
- Read satp CPU register to get PPN * 4KiB to get physical address of the root (interior) node of the mapping tree.
- Read the VPN 1 (index of the root node) of the virtual address add it to the phy. address of the root node to get the address to the corresponding PTE.
- Check if the page is valid (mapped to an physical address page ). Read the PTE to get the 22 bit page number * 4KiB to get the physical address to the leaf node.
- Read the VPN 2 (index of the leaf node) of the virtual address add it to the phy. address of the root node to get the address to the corresponding PTE.
- Check the privilege bits (RWXUV). If the page is valid and the requested access does NOT differ otherwise a page fault. Read the PTE to get the 22 bit page number * 4KiB to get the physical address to the data node. .
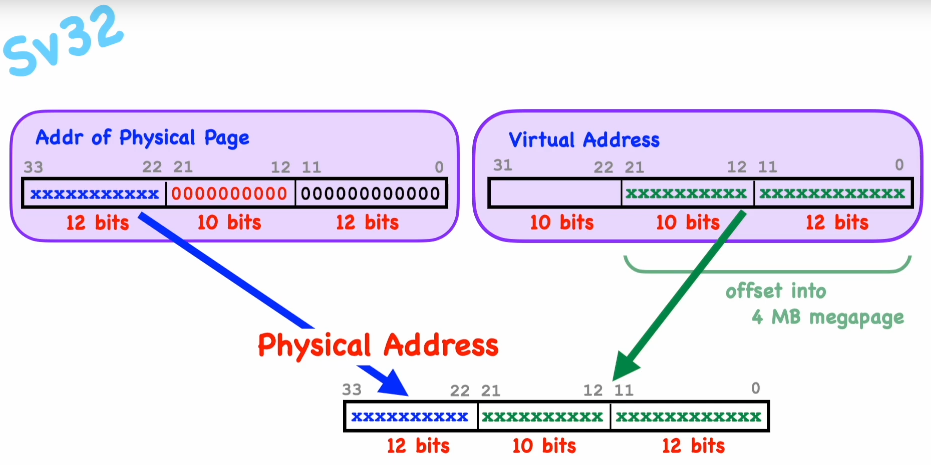
- Calculate physical address by 22 bit page number * 4KiB and add the offset (12 bit) from the virtual address.
Functional description
- address <- satp[PPN]*4
- pte -> memory [address + virtAddr[VPN_1]*4].
- If pte is not VALID, cause page fault exception. address <- pte[PPN]*4096 (a <- pte[PPN] « 12)
- pte -> memory [address + virtAddr[VPN_2]*4].
- If pte is not VALID, cause page fault exception. if pte[A] is clear, then set it. If pte[D] is clear and this is a write, then set it.
- phyAddr -> pte[PPN]*4096 + virtAddr[OFFSET]
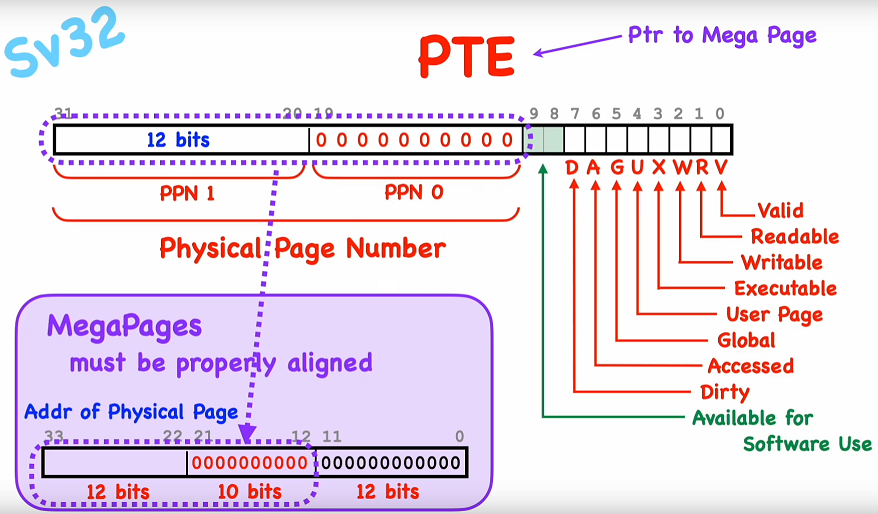
Mega pages
Size: 1KiB*4KiB = 4MiB
Addvantages:
- Reduces size of the page table
- Reduces TLB usage
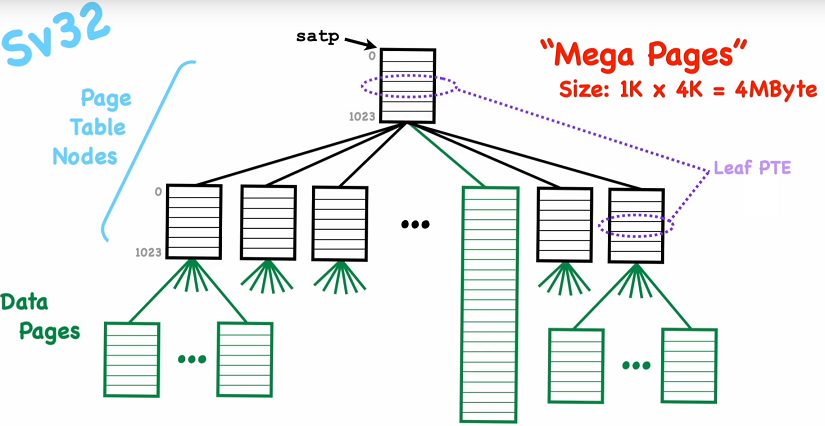
A Mega Page is a big data consisting of all data page (1024 pages) of a leaf page
merged to one data page and without a leaf entry directly managed by the root node PTE.
Physical address of a Mega Page